Hemolytic disease of the newborn, also known as Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, HDN, HDFN, or Erythroblastosis fetalis, is an alloimmune condition that develops in a fetus, when the IgG molecules (one of the five main types of antibodies) produced by the mother pass through the placenta. Among these antibodies are some which attack the red blood cells in the fetal circulation; the red cells are broken down and the fetus can develop reticulocytosis and anaemia. This fetal disease ranges from mild to very severe, and fetal death from heart failure (hydrops fetalis) can occur. When the disease is moderate or severe, many erythroblasts are present in the fetal blood and so these forms of the disease can be called erythroblastosis fetalis (or erythroblastosis foetalis).
Erythroblastosis fetalis is hemolytic anemia in the fetus or neonate caused by transplacental transmission of maternal antibodies to fetal RBCs. The disorder usually results from incompatibility between maternal and fetal blood groups, often Rh0(D) antigens. Diagnosis begins with prenatal maternal antigenic and antibody screening and may require paternal screening, serial measurement of maternal antibody titers, and fetal testing. Treatment may involve intrauterine fetal transfusion or neonatal exchange transfusion. Prevention is Rh0(D) immune globulin injection for women at risk.
Erythroblastosis fetalis classically results from Rh0(D) incompatibility, which may develop when a woman with Rh-negative blood is impregnated by a man with Rh-positive blood and conceives a fetus with Rh-positive blood (see also Perinatal Hematologic Disorders: Hemolysis). Other fetomaternal incompatibilities that can cause erythroblastosis fetalis involve the Kell, Duffy, Kidd, MNSs, Lutheran, Diego, Xg, P, Ee, and Cc antigen systems, as well as other antigens. Incompatibilities of ABO blood types do not cause erythroblastosis fetalis.
Pathophysiology
Fetal RBCs normally move across the placenta to the maternal circulation throughout pregnancy. Movement is greatest at delivery or termination of pregnancy. Movement of large volumes (eg, 10 to 150 mL) is considered significant fetomaternal hemorrhage; it can occur after trauma and sometimes after delivery or termination of pregnancy. In women who have Rh-negative blood and who are carrying a fetus with Rh-positive blood, fetal RBCs stimulate maternal antibody production against the Rh antigens. The larger the fetomaternal hemorrhage, the more antibodies produced. The mechanism is the same when other antigen systems are involved; however, Kell antibody incompatibility also directly suppresses RBC production in bone marrow.
Other causes of maternal anti-Rh antibody production include injection with needles contaminated with Rh-positive blood and inadvertent transfusion of Rh-positive blood.
No complications develop during the initial sensitizing pregnancy; however, in subsequent pregnancies, maternal antibodies cross the placenta and lyse fetal RBCs, causing anemia, hypoalbuminemia, and possibly high-output heart failure or fetal death. Anemia stimulates fetal bone marrow to produce and release immature RBCs (erythroblasts) into fetal peripheral circulation (erythroblastosis fetalis). Hemolysis results in elevated indirect bilirubin levels in neonates, causing kernicterus (see Metabolic, Electrolyte, and Toxic Disorders in Neonates: Kernicterus). Usually, isoimmunization does not cause symptoms in pregnant women.
Causes
Erythroblastosis fetalis develops in an unborn infant when the mother and baby have different blood types. The mother produces substances called antibodies that attack the developing baby's red blood cells.The most common form of erythroblastosis fetalis is ABO incompatibility, which can vary in severity.
The less common form is called Rh incompatibility, which can cause very severe anemia in the baby.
ABO incompatibility
ABO incompatibility is a reaction of the immune system that occurs if two different and not compatible blood types are mixed together.
Causes
A, B, and O are the three major blood types. The types are based on small substances (molecules) on the surface of the blood cells. In people who have different blood types, these molecules act as immune system triggers (antigens).
Each person has a combination of two of these surface molecules. Type O lacks any molecule. The different blood types are:
- Type A (AA or AO molecules)
- Type B (BB or BO molecules)
- Type AB
- Type O
People who have one blood type form proteins (antibodies) that cause their immune system to react against other blood types. Being exposed to another type of blood can cause a reaction. This is important when a patient needs to receive blood (transfusion) or have an organ transplant. The blood types must be matched to avoid an ABO incompatibility reaction.
For example:
- A patient with type A blood will react against type B or type AB blood
- A patient with type B blood will react against type A or type AB blood
- A patient with type O blood will react against type A, type B, or type AB blood
Since antibodies are in the liquid part of blood (plasma), both blood and plasma transfusions must be matched to avoid an immune reaction.
Symptoms
The following are symptoms of transfusion reactions:- Back pain
- Blood in urine
- Feeling of "impending doom"
- Fever
- Yellow skin (jaundice)
Exams and Tests
- Bilirubin level is high
- Complete blood count (CBC) shows damaged red blood cells, may also show mild anemia
- Lab testing of patient's and donor's blood shows that they are not compatible
Treatment
Treatment may include:- Drugs used to treat allergic reactions (antihistamines)
- Drugs used to treat swelling and allergies (steroids)
- Fluids given through a vein (intravenous)
- Medicines to raise blood pressure if it drops too low
Rh incompatibility
Rh incompatibility is a condition that develops when a pregnant woman has Rh-negative blood and the baby in her womb has Rh-positive blood.
Causes
During pregnancy, red blood cells from the fetus can get into the mother's bloodstream as she nourishes her child through the placenta.If the mother is Rh-negative, her immune system treats the Rh-positive fetal cells as if they were a foreign substance and makes antibodies against the fetal blood cells. These anti-Rh antibodies may cross the placenta into the developing baby, where they destroy the baby's circulating red blood cells.
When red blood cells are broken down, they make bilirubin, which causes an infant to become yellow (jaundiced). The level of bilirubin in the infant's bloodstream may range from mild to dangerously high.
Firstborn infants are often not affected -- unless the mother has had previous miscarriages or abortions, which could have sensitized her system -- as it takes time for the mother to develop antibodies against the fetal blood. However, second children who are also Rh-positive may be harmed.
Rh incompatibility develops only when the mother is Rh-negative and the infant is Rh-positive. This problem has become uncommon in the United States and other places that provide good prenatal care. Special immune globulins, called RhoGAM, are now used to prevent RH incompatibility.
Symptoms
Rh incompatibility can cause symptoms ranging from very mild to deadly. In its mildest form, Rh incompatibility causes destruction of red blood cells.Symptoms may include:
- Low muscle tone (hypotonia)
- Developmental delay
- Increased amount of amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios)
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
Exams and Tests
There may be:- A positive direct Coombs test result
- Higher than normal levels of bilirubin in the baby's cord blood
- Signs of red blood cell destruction in the infant's blood
Treatment
Since Rh incompatibility is almost completely preventable with the use of RhoGAM, prevention remains the best treatment. Treatment of the already affected infant depends on the severity of the condition.Mild Rh incompatibility may be treated with:
- Aggressive hydration
- Phototherapy using bilirubin lights
- ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALIS:
- The woman may receive a therapeutic blood transfusion. ABO blood group system and the D antigen of the Rhesus blood group system typing are routine prior to transfusion. Suggestions have been made that women of child bearing age or young girls should not be given a transfusion with Rhc-positive blood or Kell1-positive blood to avoid possible sensitization, but this would strain the resources of blood transfusion services, and it is currently considered uneconomical to screen for these blood groups. HDFN can also be caused by antibodies to a variety of other blood group system antigens, but Kell and Rh are the most frequently encountered.
- The third sensitization model can occur in women of blood type O. The immune response to A and B antigens, that are widespread in the environment, usually leads to the production of IgM anti-A and IgM anti-B antibodies early in life. On rare occasions, IgG antibodies are produced. In contrast, Rhesus antibodies are generally not produced from exposure to environmental antigens.
Serological diagnoses
- ABO system
- ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn can range from mild to severe, but generally it is a mild disease.
- anti-A antibodies
- anti-B antibodies
- ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn can range from mild to severe, but generally it is a mild disease.
- Rhesus system
- rhesus D hemolytic disease of the newborn (often called Rh disease) is the most common form of severe HDN. The disease varies from mild to severe.
- rhesus E hemolytic disease of the newborn is a mild condition
- rhesus c hemolytic disease of the newborn can range from a mild to severe disease - is the third most common form of severe HDN
- rhesus e hemolytic disease of the newborn - rare
- rhesus C hemolytic disease of the newborn - rare
- antibody combinations (ie anti-Rhc and anti-RhE antibodies occurring together) - can be severe
- Kell system
- anti-Kell hemolytic disease of the newborn
- anti-K 1 antibodies - disease ranges from mild to severe - over half of the cases are caused by multiple blood transfusions - is the second most common form of severe HDN
- anti-K 2 ,anti-K 3 and anti-K 4 antibodies - rare
- anti-Kell hemolytic disease of the newborn
- Other blood group antibodies
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of HDN is based on history and laboratory findings:
Blood tests done on the newborn baby
- Biochemistry tests for jaundice
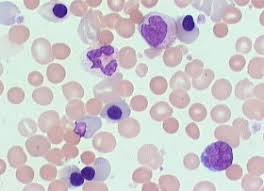
- Peripheral blood morphology shows increased reticulocytes. Erythroblasts (also known as nucleated red blood cells) occur in moderate and severe disease.
- Positive direct Coombs test (might be negative after fetal interuterine blood transfusion)
- Positive indirect Coombs test
Treatment
Before birth, options for treatment include intrauterine transfusion or early induction of labor when pulmonary maturity has been attained, fetal distress is present, or 35 to 37 weeks of gestation have passed. The mother may also undergo plasma exchange to reduce the circulating levels of antibody by as much as 75%.
After birth, treatment depends on the severity of the condition, but could include temperature stabilization and monitoring, phototherapy, transfusion with compatible packed red blood, exchange transfusion with a blood type compatible with both the infant and the mother, sodium bicarbonate for correction of acidosis and/or assisted ventilation.
Rhesus-negative mothers who have had a pregnancy with/are pregnant with a rhesus-positive infant are given Rh immune globulin (RhIG) at 28 weeks during pregnancy and within 72 hours after delivery to prevent sensitization to the D antigen. It works by binding any fetal red cells with the D antigen before the mother is able to produce an immune response and form anti-D IgG. A drawback to pre-partum administration of RhIG is that it causes a positive antibody screen when the mother is tested, which can be difficult to distinguish from natural immunonological responses that result in antibody production.
Complications
Complications of HDN could include kernicterus, hepatosplenomegaly, inspissated (thickened or dried) bile syndrome and/or greenish staining of the teeth, hemolytic anemia and damage to the liver due to excess bilirubin.
Similar conditions
Similar conditions include acquired hemolytic anemia, congenital toxoplasma and syphilis infection, congenital obstruction of the bile duct and cytomegalovirus infection.
In animals
Hemolytic disease is a well-known condition in newborn foals, especially in Thoroughbreds and mules. Mares or jennies which have been sensitized by a previous pregnancy develop antibodies by fetal blood cells crossing the placental barrier. The iso-antibodies do not transcend the fetal barrier, but are present in colostrum. They will enter the bloodstream of the foal only after absorption of colostrum immunoglobulins, in the first days of life. Hence, hemolytic disaese will develop only after birth : first to 4th day in foal and 3 to 7 days in newborn mules.
Affected animals show lethargy, recumbency, tachycardia, and progressive icterus of eye and mouth mucosae, which rapidly leads to death.
The condition is also described in newborn pigs and other animals




can I get the references for this article
ReplyDeleteAll thanks to this great herbal doctor who cured me from (LUPUS DISEASE) his name is dr imoloa. I suffered lupus disease for over 8 years with pains like: joints, Skin rash, Pain in the chest, swollen joints and many more. The anti-inflammatory drugs couldn’t cure me, until I read about his recommendation. 2 months ago, I contacted him through his email address. drimolaherbalmademedicine@gmail.com . and he sent me the herbal treatment through DHL courier service and he instructed me on how to drink it for good two weeks. after then, And I was confirmed cured and free at the hospital after taken his powerful herbal medications You too can be cured with it if interested, he also uses his powerful herbal healing medicine to cure disease like:parkison disease, vaginal cancer, epilepsy, Anxiety Disorders, Autoimmune Disease, Back Pain, Back Sprain, Bipolar Disorder, Brain Tumour, Malignant, Bruxism, Bulimia, Cervical Disk Disease, cardiovascular disease, Neoplasms, chronic respiratory disease, mental and behavioural disorder, Cystic Fibrosis, Hypertension, Diabetes, asthma, Inflammatory autoimmune-mediated arthritis. chronic kidney disease, inflammatory joint disease, back pain, impotence, feta alcohol spectrum, Dysthymic Disorder, Eczema, skin cancer, tuberculosis, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, constipation, inflammatory bowel disease, bone cancer, lungs cancer, mouth ulcer, mouth cancer, body pain, fever, hepatitis A.B.C., syphilis, diarrhea, HIV/AIDS, Huntington's Disease, back acne, Chronic renal failure, addison disease, Chronic Pain, Crohn's Disease, Cystic Fibrosis, Fibromyalgia, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, fungal nail disease, Lyme Disease, Celia disease, Lymphoma, Major Depression, Malignant Melanoma, Mania, Melorheostosis, Meniere's Disease, Mucopolysaccharidosis , Multiple Sclerosis, Muscular Dystrophy, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Alzheimer's Disease Contacts him today and get permanently cure. contact him via... email- drimolaherbalmademedicine@gmail.com /whatssapp-+2347081986098.
ReplyDeleteChemicals used in industries gives me Leukemia and it's all started when I wanted to get off my job to get another job that when I got diagnose, at that very point I was so scared to die because it has infected my blood cells also I was prescribed drugs like Cyclophosphamide,Busulfan,Bosutinib,Cytarabine, Cytosar-U (Cytarabine),Dasatinib in all that was just to keep me waiting for my dying day. I got inspired by what I read from a lady on blog spot on how Dr God hands cure her HIV/Aids with herbal medicine then they were lettered below that says he can cure Cancer so I pick his contact on the testimony she wrote then I emailed Dr God hands hopefully he replied swiftly to my mail then I purchased his Herbal medicine also it was shipped to me here in Texas, I went to pick it at post office so he instructs me on how the treatment will take me three weeks to cure my Leukemia Disease, Joyfully I was cured by this Dr God hands Herbal Medicine.
ReplyDeleteI will advise you too to give a try to Dr God hands Herbal Medicine with the following diseases that he can help you cure permanently such diabetes, Herpes, HIV/Aids, Bladder Cancer, Breast Cancer,Parkinson's disease,Lung Cancer, Breast Cancer, Colo-Rectal Cancer, Blood Cancer, Prostate Cancer,Arthritis,Fibromyalgia,Adrenocortical carcinoma. Asthma, Cold, Glaucoma, Cardiovascular disease, Lung disease, Enlarged prostate, Alzheimer's disease, Dementia, Vaginal Cancer, Kidney Cancer, Lung Cancer, Skin Cancer, Uterine Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Colo_Rectal Cancer, Leukemia Cancer, Hepatitis, Brain Tumors, Love Spell, Infertility, Hpv. GoodLuck, XoXo****Dr Owo Ibuku Also known as Doctor God hands Contact Information:::Email (doctorgodhands@gmail.com) WhatsApp-(+2349057214220)
I was diagnosed as HEPATITIS B carrier in 2013 with fibrosis of the
ReplyDeleteliver already present. I started on antiviral medications which
reduced the viral load initially. After a couple of years the virus
became resistant. I started on HEPATITIS B Herbal treatment from
ULTIMATE LIFE CLINIC (www.ultimatelifeclinic.com) in March, 2020. Their
treatment totally reversed the virus. I did another blood test after
the 6 months long treatment and tested negative to the virus. Amazing
treatment! This treatment is a breakthrough for all HBV carriers.